Programmers Love Writing Tests
| Test Infected:
Programmers Love Writing Tests |
 |
Kent Beck,
CSLife
Erich Gamma,
OTI Zürich
Testing is not closely integrated with development. This prevents you from measuring the progress of development- you can't tell when something starts working or when something stops working. Using JUnit you can cheaply and incrementally build a test suite that will help you measure your progress, spot unintended side effects, and focus your development efforts.
Programmers burn out from just such cycles. Breaking out requires an outside influence. We found the outside influence we needed in a simple testing framework that lets us do a little testing that makes a big difference.
The best way to convince you of the value of writing your own tests would be to sit down with you and do a bit of development. Along the way, we would encounter new bugs, catch them with tests, fix them, have them come back, fix them again, and so on. You would see the value of the immediate feedback you get from writing and saving and rerunning your own unit tests.
Unfortunately, this is an article, not an office overlooking charming old-town Zürich, with the bustle of medieval commerce outside and the thump of techno from the record store downstairs, so we'll have to simulate the process of development. We'll write a simple program and its tests, and show you the results of running the tests. This way you can get a feel for the process we use and advocate without having to pay for our presence.
The program we write will solve the problem of representing arithmetic with multiple currencies. Arithmetic between single currencies is trivial, you can just add the two amounts. Simple numbers suffice. You can ignore the presence of currencies altogether.
Things get more interesting once multiple currencies are involved. You cannot just convert one currency into another for doing arithmetic since there is no single conversion rate- you may need to compare the value of a portfolio at yesterday's rate and today's rate.
Let's start simple and define a class Money to represent a value in a single currency. We represent the amount by a simple int. To get full accuracy you would probably use double or java.math.BigDecimal to store arbitrary-precision signed decimal numbers. We represent a currency as a string holding the ISO three letter abbreviation (USD, CHF, etc.). In more complex implementations, currency might deserve its own object.
class Money {
private int fAmount;
private String fCurrency;
public Money(int amount, String currency) {
fAmount= amount;
fCurrency= currency;
}
public int amount() {
return fAmount;
}
public String currency() {
return fCurrency;
}
}
When you add two Moneys of the same currency, the
resulting Money has as its amount the sum of the other two amounts.
public Money add(Money m) {
return new Money(amount()+m.amount(), currency());
}
Now, instead of just coding on, we want to get immediate feedback and practice
"code a little, test a little, code a little, test a little". To implement
our tests we use the JUnit framework. To write tests you need to get the
latest copy
JUnit (or write your own equivalent- it's not so much work).
JUnit defines how to structure your test cases and provides the tools to run them. You implement a test in a subclass of TestCase. To test our Money implementation we therefore define MoneyTest as a subclass of TestCase. In Java, classes are contained in packages and we have to decide where to put MoneyTest. Our current practice is to put MoneyTest in the same package as the classes under test. In this way a test case has access to the package private methods. We add a test method testSimpleAdd, that will exercise the simple version of Money.add() above. A JUnit test method is an ordinary method without any parameters.
public class MoneyTest extends TestCase {
//…
public void testSimpleAdd() {
Money m12CHF= new Money(12, "CHF"); // (1)
Money m14CHF= new Money(14, "CHF");
Money expected= new Money(26, "CHF");
Money result= m12CHF.add(m14CHF); // (2)
assert(expected.equals(result)); // (3)
}
}
The testSimpleAdd() test case consists of:
public void testEquals() {
Money m12CHF= new Money(12, "CHF");
Money m14CHF= new Money(14, "CHF");
assert(!m12CHF.equals(null));
assert(m12CHF, m12CHF);
assertEquals(m12CHF, new Money(12, "CHF")); // (1)
assert(!m12CHF.equals(m14CHF));
}
The equals method in Object returns true when both objects are the same.
However, Money is a value object. Two Monies are considered equal
if they have the same currency and value. To test this property we have
added a test (1) to verify that Monies are equal
when they have the same value but are not the same object.
Next let's write the equals method in Money:
public boolean equals(Object anObject) {
if (! anObject instanceof Money)
return false;
Money aMoney= (Money)anObject;
return aMoney.currency().equals(currency())
&& amount() == aMoney.amount();
}
Since equals can receive any kind of object as its argument we first have
to check its type before we cast it as a Money. As an aside, it is a recommended
practice to also override the method hashCode whenever you override method
equals. However, we want to get back to our test case.
With an equals method in hand we can verify the outcome of testSimpleAdd. In JUnit you do so by a calling assert which is inherited from TestCase. Assert triggers a failure that is logged by JUnit when the argument isn't true. Since assertions for equality are very common, TestCase also defines an assertEquals convenience method. In addition to testing for equality with equals, it logs the printed value of the two objects in the case they differ. This lets us immediately see why a test failed in a JUnit test result report. The value is logged as a string representation created by the toString converter method.
Now that we have implemented two test cases we notice some code duplication for setting-up the tests. It would be nice to reuse some of this test set-up code. In other words, we would like to have a common fixture for running the tests. With JUnit you can do so by storing the fixture's objects in instance variables of your TestCase class and initialize them by overridding the setUp method. The symmetric operation to setUp is tearDown which you can override to clean up the test fixture at the end of a test. Each test runs in its own fixture and JUnit calls setUp and tearDown for each test so that there can be no side effects among test runs.
public class MoneyTest extends TestCase {
private Money f12CHF;
private Money f14CHF;
protected void setUp() {
f12CHF= new Money(12, "CHF");
f14CHF= new Money(14, "CHF");
}
}
We can rewrite the two test case methods, removing the common setup code:
public void testEquals() {
assert(!f12CHF.equals(null));
assertEquals(f12CHF, f12CHF);
assertEquals(m12CHF, new Money(12, "CHF"));
assert(!f12CHF.equals(f14CHF));
}
public void testSimpleAdd() {
Money expected= new Money(26, "CHF");
Money result= f12CHF.add(f14CHF);
assert(expected.equals(result));
}
Two additional steps are needed to run the two test cases:
TestCase test= new MoneyTest("simple add") {
public void runTest() {
testSimpleAdd();
}
};
A template method[1]
in the superclass will make sure runTest is executed when the time comes.
The dynamic way to create a test case to be run uses reflection to implement runTest. It assumes the name of the test is the name of the test case method to invoke. It dynamically finds and invokes the test method. To invoke the testSimpleAdd test we therefore construct a MoneyTest as shown below:
TestCase = new MoneyTest("testSimpleAdd");
The dynamic way is more compact to write but it is less static type safe.
An error in the name of the test case goes unnoticed until you run it and
get a NoSuchMethodException. Since both approaches have advantages, we
decided to leave the choice of which to use up to you.
As the last step to getting both test cases to run together, we have to define a test suite. In JUnit this requires the definition of a static method called suite. The suite method is like a main method that is specialized to run tests. Inside suite you add the tests to be run to a TestSuite object and return it. A TestSuite can run a collection of tests. TestSuite and TestCase both implement an interface called Test which defines the methods to run a test. This enables the creation of test suites by composing arbitrary TestCases and TestSuites. In short TestSuite is a Composite [1]. The code below illustrates the creation of a test suite with the dynamic way to run a test.
public static Test suite() {
TestSuite suite= new TestSuite();
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testMoneyEquals"));
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testSimpleAdd"));
return suite;
}
Here is the corresponding code using the static way.
public static Test suite() {
TestSuite suite= new TestSuite();
suite.addTest(
new MoneyTest("money equals") {
protected void runTest() { testMoneyEquals(); }
}
);
suite.addTest(
new MoneyTest("simple add") {
protected void runTest() { testSimpleAdd(); }
}
);
return suite;
}
Now we are ready to run our tests. JUnit comes with a graphical interface
to run tests. Type the name of your test class in the field at the top
of the window. Press the Run button. While the test is run JUnit shows
its progress with a progress bar below the input field. The bar is initially
green but turns into red as soon as there is an unsuccessful test. Failed
tests are shown in a list at the bottom. Figure 1
shows the TestRunner window after we run our trivial test suite.

After having verified that the simple currency case works we move on to multiple currencies. As mentioned above the problem of mixed currency arithmetic is that there isn't a single exchange rate. To avoid this problem we introduce a MoneyBag which defers exchange rate conversions. For example adding 12 Swiss Francs to 14 US Dollars is represented as a bag containing the two Monies 12 CHF and 14 USD. Adding another 10 Swiss francs gives a bag with 22 CHF and 14 USD. We can later evaluate a MoneyBag with different exchange rates.
A MoneyBag is represented as a list of Monies and provides different constructors to create a MoneyBag. Note, that the constructors are package private since MoneyBags are created behind the scenes when doing currency arithmetic.
class MoneyBag {
private Vector fMonies= new Vector();
MoneyBag(Money m1, Money m2) {
appendMoney(m1);
appendMoney(m2);
}
MoneyBag(Money bag[]) {
for (int i= 0; i < bag.length; i++)
appendMoney(bag[i]);
}
}
The method appendMoney is an internal helper method that adds a Money to
the list of Moneys and takes care of consolidating Monies with the same
currency. MoneyBag also needs an equals method together with a corresponding
test. We skip the implementation of equals and only show the testBagEquals
method. In a first step we extend the fixture to include two MoneyBags.
protected void setUp() {
f12CHF= new Money(12, "CHF");
f14CHF= new Money(14, "CHF");
f7USD= new Money( 7, "USD");
f21USD= new Money(21, "USD");
fMB1= new MoneyBag(f12CHF, f7USD);
fMB2= new MoneyBag(f14CHF, f21USD);
}
With this fixture the testBagEquals test case becomes:
public void testBagEquals() {
assert(!fMB1.equals(null));
assertEquals(fMB1, fMB1);
assert(!fMB1.equals(f12CHF));
assert(!f12CHF.equals(fMB1));
assert(!fMB1.equals(fMB2));
}
Following "code a little, test a little" we run our extended test with
JUnit and verify that we are still doing fine. With MoneyBag in hand, we
can now fix the add method in Money.
public Money add(Money m) {
if (m.currency().equals(currency()) )
return new Money(amount()+m.amount(), currency());
return new MoneyBag(this, m);
}
As defined above this method will not compile since it expects a Money
and not a MoneyBag as its return value. With the introduction of MoneyBag
there are now two representations for Moneys which we would like to hide
from the client code. To do so we introduce an interface IMoney that both
representations implement. Here is the IMoney interface:
interface IMoney {
public abstract IMoney add(IMoney aMoney);
//…
}
To fully hide the different representations from the client we have to
support arithmetic between all combinations of Moneys with MoneyBags. Before
we code on, we therefore define a couple more test cases. The expected
MoneyBag results use the convenience constructor shown above, initializing
a MoneyBag from an array.
public void testMixedSimpleAdd() {
// [12 CHF] + [7 USD] == {[12 CHF][7 USD]}
Money bag[]= { f12CHF, f7USD };
MoneyBag expected= new MoneyBag(bag);
assertEquals(expected, f12CHF.add(f7USD));
}
The other tests follow the same pattern:
Next, we extend our test suite accordingly:
public static Test suite() {
TestSuite suite= new TestSuite();
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testMoneyEquals"));
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testBagEquals"));
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testSimpleAdd"));
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testMixedSimpleAdd"));
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testBagSimpleAdd"));
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testSimpleBagAdd"));
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testBagBagAdd"));
return suite;
}
Having defined the test cases we can start to implement them. The implementation
challenge here is dealing with all the different combinations of Money
with MoneyBag. Double dispatch [2]
is an elegant way to solve this problem. The idea behind double dispatch
is to use an additional call to discover the kind of argument we are dealing
with. We call a method on the argument with the name of the original method
followed by the class name of the receiver. The add method in Money and
MoneyBag becomes:
class Money implements IMoney {
public IMoney add(IMoney m) {
return m.addMoney(this);
}
//…
}
class MoneyBag implements IMoney {
public IMoney MoneyBag.add(IMoney m) {
return m.addMoneyBag(this);
}
//…
}
In order to get this to compile we need to extend the interface of IMoney
with the two helper methods:
interface IMoney {
//…
IMoney addMoney(Money aMoney);
IMoney addMoneyBag(MoneyBag aMoneyBag);
}
To complete the implementation of double dispatch, we have to implement
these methods in Money and MoneyBag. This is the implementation in Money.
public IMoney addMoney(Money m) {
if (m.currency().equals(currency()) )
return new Money(amount()+m.amount(), currency());
return new MoneyBag(this, m);
}
public IMoney addMoneyBag(MoneyBag s) {
return s.addMoney(this);
}
Here is the implemenation in MoneyBag which assumes additional constructors
to create a MoneyBag from a Money and a MoneyBag and from two MoneyBags.
public IMoney addMoney(Money m) {
return new MoneyBag(m, this);
}
public IMoney addMoneyBag(MoneyBag s) {
return new MoneyBag(s, this);
}
We run the tests, and they pass. However, while reflecting on the implementation
we discover another interesting case. What happens when as the result of
an addition a MoneyBag turns into a bag with only one Money? For example,
adding -12 CHF to a Moneybag holding 7 USD and 12 CHF results in a bag
with just 7 USD. Obviously, such a bag should be equal with a single Money
of 7 USD. To verify the problem let's implement a test case and run it.
public void testSimplify() {
// {[12 CHF][7 USD]} + [-12 CHF] == [7 USD]
Money expected= new Money(7, "USD");
assertEquals(expected, fMS1.add(new Money(-12, "CHF")));
}
When you are developing in this style you will often have a thought and
turn immediately to writing a test, rather than going straight to the code.
It comes to no surprise that our test run ends with a red progress bar indicating the failure. So we fix the code in MoneyBag to get back to a green state.
public IMoney addMoney(Money m) {
return (new MoneyBag(m, this)).simplify();
}
public IMoney addMoneyBag(MoneyBag s) {
return (new MoneyBag(s, this)).simplify();
}
private IMoney simplify() {
if (fMonies.size() == 1)
return (IMoney)fMonies.firstElement()
return this;
}
Now we run our tests again and voila we end up with green.
The code above solves only a small portion of the multi-currency arithmetic problem. We have to represent different exchange rates, print formatting, and the other arithmetic operations, and do it all with reasonable speed. However, we hope you can see how you could develop the rest of the objects one test at a time- a little test, a little code, a little test, a little code.
In particular, review how in the development above:
The simplest way is as an expression in a debugger. You can change debug expressions without recompiling, and you can wait to decide what to write until you have seen the running objects. You can also write test expressions as statements which print to the standard output stream. Both styles of tests are limited because they require human judgement to analyze their results. Also, they don't compose nicely- you can only execute one debug expression at a time and a program with too many print statements causes the dreaded "Scroll Blindness".
JUnit tests do not require human judgement to interpret, and it is easy to run many of them at the same time. When you need to test something, here is what you do:
public void testSimpleAdd() {
Money m12CHF= new Money(12, "CHF");
Money m14CHF= new Money(14, "CHF");
Money expected= new Money(26, "CHF");
Money result= m12CHF.add(m14CHF);
assert(expected.equals(result));
}
If you want to write a test similar to one you have already written, write
a Fixture instead. When you want to run more than
one test, create a Suite.
Tests need to run against the background of a known set of objects. This set of objects is called a test fixture. When you are writing tests you will often find that you spend more time writing the code to set up the fixture than you do in actually testing values.
To some extent, you can make writing the fixture code easier by paying careful attention to the constructors you write. However, a much bigger savings comes from sharing fixture code. Often, you will be able to use the same fixture for several different tests. Each case will send slightly different messages or parameters to the fixture and will check for different results.
When you have a common fixture, here is what you do:
public class MoneyTest extends TestCase {
private Money f12CHF;
private Money f14CHF;
private Money f28USD;
protected void setUp() {
f12CHF= new Money(12, "CHF");
f14CHF= new Money(14, "CHF");
f28USD= new Money(28, "USD");
}
}
Once you have the Fixture in place, you can write as many Test
Cases as you'd like.
Writing a test case without a fixture is simple- override runTest() in an anonymous subclass of TestCase. You write test cases for a Fixture the same way, by making a subclass of TestCase for your set up code and then making anonymous subclasses for the individual test cases. However, after a few such tests you would notice that a large percentage of your lines of code are sacrificed to syntax.
JUnit provides a more concise way to write a test against a Fixture. Here is what you do:
public void testMoneyMoneyBag() {
// [12 CHF] + [14 CHF] + [28 USD] == {[26 CHF][28 USD]}
Money bag[]= { f26CHF, f28USD };
MoneyBag expected= new MoneyBag(bag);
assertEquals(expected, f12CHF.add(f28USD.add(f14CHF)));
}
Create an instance of of MoneyTest that will run this test case like this:
new MoneyTest("testMoneyMoneyBag")
When the test is run, the name of the test is used to look up the method
to run.
Once you have several tests, organize them into a Suite.
As soon as you have two tests, you'll want to run them together. You could run the tests one at a time yourself, but you would quickly grow tired of that. Instead, JUnit provides an object, TestSuite which runs any number of TestCases together.
For example, to run a single test case, you execute:
TestResult result= (new MoneyTest("testMoneyMoneyBag")).run();
To create a suite of two test cases and run them together, execute:
TestSuite suite= new TestSuite();
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testMoneyEquals"));
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testSimpleAdd"));
TestResult result= suite.run();
TestSuites don't only have to contain TestCases. They contain any object
that implements the Test interface. For example, you can create a TestSuite
in your code and I can create one in mine, and we can run them together
by creating a TestSuite that contains both:
TestSuite suite= new TestSuite(); suite.addTest(Kent.suite()); suite.addTest(Erich.suite()); TestResult result= suite.run();
Once you have a test suite, you'll want to run it. JUnit provides tools to define the suite to be run and to display its results. You make your suite accessible to a TestRunner tool with a static method suite that returns a test suite. For example, to make a MoneyTest suite available to a TestRunner, add the following code to MoneyTest:
public static Test suite() {
TestSuite suite= new TestSuite();
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testMoneyEquals"));
suite.addTest(new MoneyTest("testSimpleAdd"));
return suite;
}
JUnit provides both a graphical and a textual version of a TestRunner tool.
Start it by typing java test.ui.TestRunner.
The graphical user interface presents a window with:
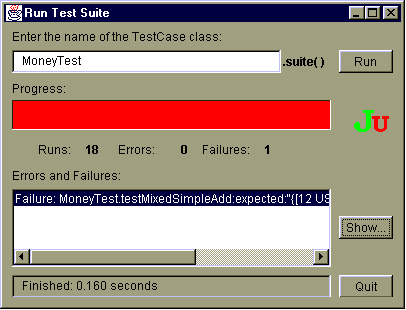
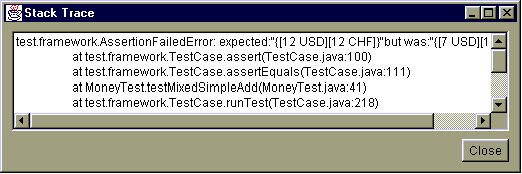
To find out more about a failure or an error select it in the list and press Show. This will show you a stack trace of the failure (Figure 3).
Note that you can leave the JUnit window up all the time. After every compile, press Run and JUnit will load the latest versions of your test classes.
There is a batch interface to JUnit, also. To use it type java test.textui.TestRunner followed by the name of the class with a suite method at an operating system prompt. The batch interface shows the result as text output. An alternative way to invoke the batch interface is to define a main method in your TestCase class.
For example, to start the batch TestRunner for MoneyTest, write:
public static void main(String args[]) {
test.textui.TestRunner.run(suite());
}
With this definition of main you can run your tests by simply typing java
MoneyTest at an operating system prompt.
For using either the graphical or the textual version make sure that the test.jar file is on your CLASSPATH.
You can always write more tests. However, you will quickly find that only a fraction of the tests you can imagine are actually useful. What you want is to write tests that fail even though you think they should work, or tests that succeed even though you think they should fail. Another way to think of it is in cost/benefit terms. You want to write tests that will pay you back with information.
Here are a couple of the times that you will receive a reasonable return on your testing investment:
Once you've been test infected, your attitude toward development is likely to change. Here are some of the changes we have noticed:
There is a huge difference between tests that are all running correctly and tests that aren't. Part of being test infected is not being able to go home if your tests aren't 100%. If you run your suite ten or a hundred times an hour, though, you won't be able to create enough havoc to make you late for supper.
Sometimes you just won't feel like writing tests, especially at first. Don't. However, pay attention to how much more trouble you get into, how much more time you spend debugging, and how much more stress you feel when you don't have tests. We have been amazed at how much more fun programming is and how much more aggressive we are willing to be and how much less stress we feel when we are supported by tests. The difference is dramatic enough to keep us writing tests even when we don't feel like it.
You will be able to refactor much more aggressively once you have the tests. You won't understand at first just how much you can do, though. Try to catch yourself saying, "Oh, I see, I should have designed this thus and so. I can't change it now. I don't want to break anything." When you say this, save a copy of your current code and give yourself a couple of hours to clean up. (This part works best you can get a buddy to look over your shoulder while you work.) Make your changes, all the while running your tests. You will be surprised at how much ground you can cover in a couple of hours if you aren't worrying every second about what you might be breaking.
For example, we switched from the Vector-based implementation of MoneyBag to one based on HashTable. We were able to make the switch very quickly and confidently because we had so many tests to rely on. If the tests all worked, we were sure we hadn't changed the answers the system produced at all.
You will want to get the rest of your team writing tests. The best way we have found to spread the test infection is through direct contact. The next time someone asks you for help debugging, get them to talk about the problem in terms of a fixture and expected results. Then say, "I'd like to write down what you just told me in a form we can use." Have them watch while you write one little test. Run it. Fix it. Write another. Pretty soon they will be writing their own.
So- give JUnit a try. If you make it better, please send us the changes so we can spread them around. Our next article will double click on the JUnit framework itself. We will show you how it is constructed, and talk a little about our philosophy of framework development.
We would like to thank Martin Fowler, as good a programmer as any analyst can ever hope to be, for his helpful comments in spite of being subjected to early versions of JUnit.